The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program, administered by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), is a unique initiative designed to stimulate economic growth, job creation, and capital investment by granting immigrant visas to foreign investors who meet specific capital investment and job creation requirements. In this blog, we will provide a comprehensive research guide to help you understand how the EB-5 Program works, supported by reliable data and facts.
The EB-5 Program, created by the Immigration Act of 1990, offers two main investment pathways:
- Direct Investment: Investors establish a new commercial enterprise or invest in an existing one.
- Regional Center Investment: Investors invest in a U.S. government-approved Regional Center, which facilitates job creation and economic development in a specific geographic area.
According to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), the EB-5 Program has attracted billions of dollars in foreign investment, contributing to U.S. job creation and economic growth. The program allocates up to 10,000 visas annually for eligible investors and their family members.
Part II: Investment Amounts and Job Creation Requirements
To qualify for the EB-5 Program, investors must meet specific investment and job creation criteria:
- Minimum Investment: Investors must invest $1.8 million in a new commercial enterprise. If the investment is in a Targeted Employment Area (TEA), which is either a rural area or an area with high unemployment, the minimum investment is reduced to $900,000.
As of September 2021, USCIS increased the minimum investment amounts for the EB-5 Program, taking inflation into account.
Part III: The Role of Regional Centers
According to Invest in the USA (IIUSA), there were 1,053 USCIS-approved regional centers in the United States in 2020, indicating the widespread utilization of regional centers to attract EB-5 investments.
Part IV: The EB-5 Application Process
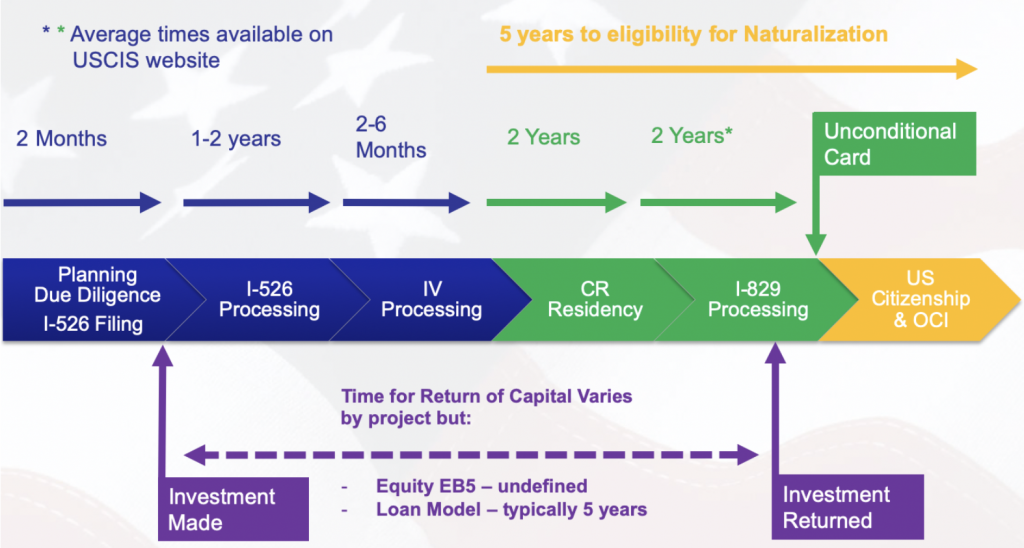
The EB-5 application process involves the following key steps:
I-526 Petition: Investors submit an I-526 Immigrant Petition by Alien Investor to USCIS, providing documentation to prove their investment's legality and the source of their funds.
The processing time for I-526 petitions can vary but typically takes around 29 months, as reported by USCIS.
Conditional Green Card: If the I-526 petition is approved, investors and their immediate family members are granted conditional green cards.
Part V: Conditions Removal and Permanent Green Card
To obtain a permanent green card, investors must file an I-829 Petition to Remove Conditions on Residence within the 90-day window before the second anniversary of receiving their conditional green cards. They must prove that they met the investment and job creation requirements.
According to the USCIS, the processing time for I-829 petitions typically takes around 34 months.
Part VI: Investment Outcomes and Benefits
EB-5 investments can lead to permanent U.S. residency for the investor, their spouse, and unmarried children under 21. It can also offer potential financial returns, but investors should be aware of the risks involved.
The Migration Policy Institute reports that EB-5 investors have contributed significantly to real estate and development projects, particularly in urban areas.
The EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program offers a unique opportunity for foreign investors to obtain U.S. permanent residency while stimulating job creation and economic growth in the United States. Understanding the program's requirements, investment options, and application process is essential for those considering participation. With reliable data and sources as your guide, you can make well-informed decisions about whether the EB-5 Program aligns with your investment and immigration goals.
